Harness the full potential of
Industry 4.0
Greater Flexibility in Processes, Increased Productivity and Revenue, and Higher-Quality Production.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industrialization has seen revolution after revolutions in every decade since its evolution in the 18th century. From the advent of steam power inventions to the introduction of electricity a century later, to the third industrial revolution in the 1970’s with the advances in computing, till today where Industry 4.0 has brought in the fourth Industrial Revolution that is transforming the economy, jobs, and society.
Industry 4.0 is a recent technological advances where automation, data exchange, cyber-physical systems, Internet of things, cloud, Big Data and cognitive computing comes together to form the fourth technological revolution.
Start your imaginations
Glimpse into an Industry 4.0 Digital Transformation Journey
Smart Manufacturing:
At the heart of Industry 4.0 is the smart factory where machine intelligence, advanced networking, and real-time controls enable manufacturers to respond to disruptive trends, enter new markets, deliver better products, and get ahead of operational challenges.
Pillars of IR4.0

Harness the full potential of
Industry 4.0
Greater Flexibility in Processes, Increased Productivity and Revenue, and Higher-Quality Production. That's Achieved by makes factories “smart.” using technologies such as the industrial Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and cyber-physical systems.
Key Technologies Empowering Smart Manufacturing:
The classic example of additive manufacturing is 3D printing. Instead of prototyping individual components, companies can now produce small batches of customized products. The resulting advantages include the speedy manufacturing of complex, lightweight designs.
Augmented reality (AR) systems support a variety of services, such as selecting parts in a warehouse and sending repair instructions over mobile devices. With AR, companies can provide workers with real-time information that improves decision making and work procedures.
Autonomous robots can interact with one another and work safely side by side with humans. These robots will cost less and have an increasing range of capabilities over time.
In an Industry 4.0 context, the collection and comprehensive evaluation of data from many different sources—production equipment and systems as well as enterprise- and customer-management systems—will become table stakes.
The more production-related initiatives a company undertakes, the more it needs to share data across sites. Meanwhile, cloud technologies continue to get faster and more powerful. Companies will increasingly deploy machine data and analytics to the cloud, thus enabling more data-driven services for production systems.
It’s no surprise that Industry 4.0 boosts increased connectivity and the use of standard communications protocols. As a result, the need to protect critical industrial systems and manufacturing lines from cybersecurity threats rises dramatically. For this reason, secure, reliable communications, together with sophisticated access management for machines and identity verification of users, are essential.
Industry 4.0 allows companies, departments, functions, and capabilities to become much more cohesive. Cross-company, universal data-integration networks evolve and enable truly automated value chains.
Industry 4.0 means that more devices are enriched with embedded computing. This process allows devices to communicate and interact both with one another and with more centralized controllers. It also decentralizes analytics and decision making, thus enabling responses in real time.
Simulations are a cornerstone of the industrial revolution 4.0. They’re used extensively in plant operations to leverage real-time data and to mirror the physical world. Done right, these models allow operators to test and optimize settings in numerous variations, thereby driving down machine setup times and increasing quality.
IoT Solutions for Smart Manufacturing
The Industrial IoT extends Information Technology (IT) to Operational Technology (OT), adding intelligence to manufacturing equipment, processes, and management.
Our smart manufacturing solutions use connected sensors and devices at the network edge to improve machine and human performance in real-time, and pass data to the cloud for deeper analysis and insights. Welcome to Industry 4.0.
Key factors in digital factory transformation
Connectivity
processes, machines, and people are connected to improve efficiency.

Optimization
high levels of automation to increase uptime and productivity.
Agility
configurable factory layouts and implementation of product changes in real-time.

Transparency
visibility across all operations to allow real-time decision making.
Proactive
automated re-stocking, fault detection, and safety monitoring.
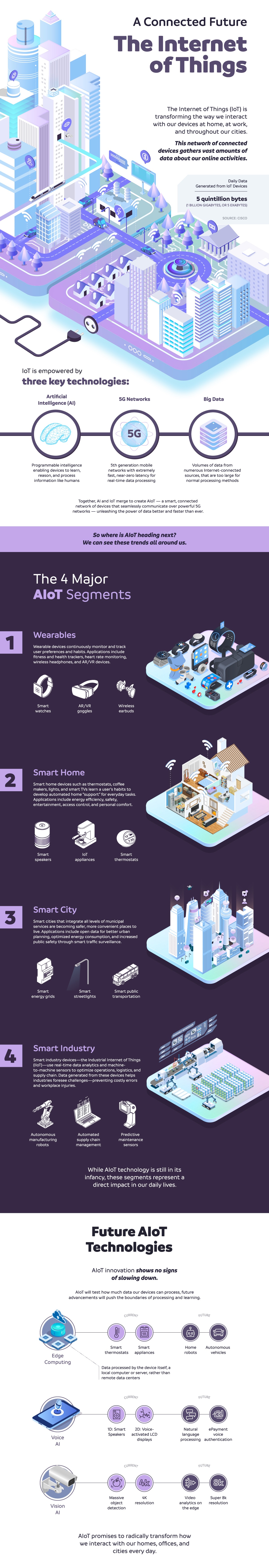
* visualcapitalist