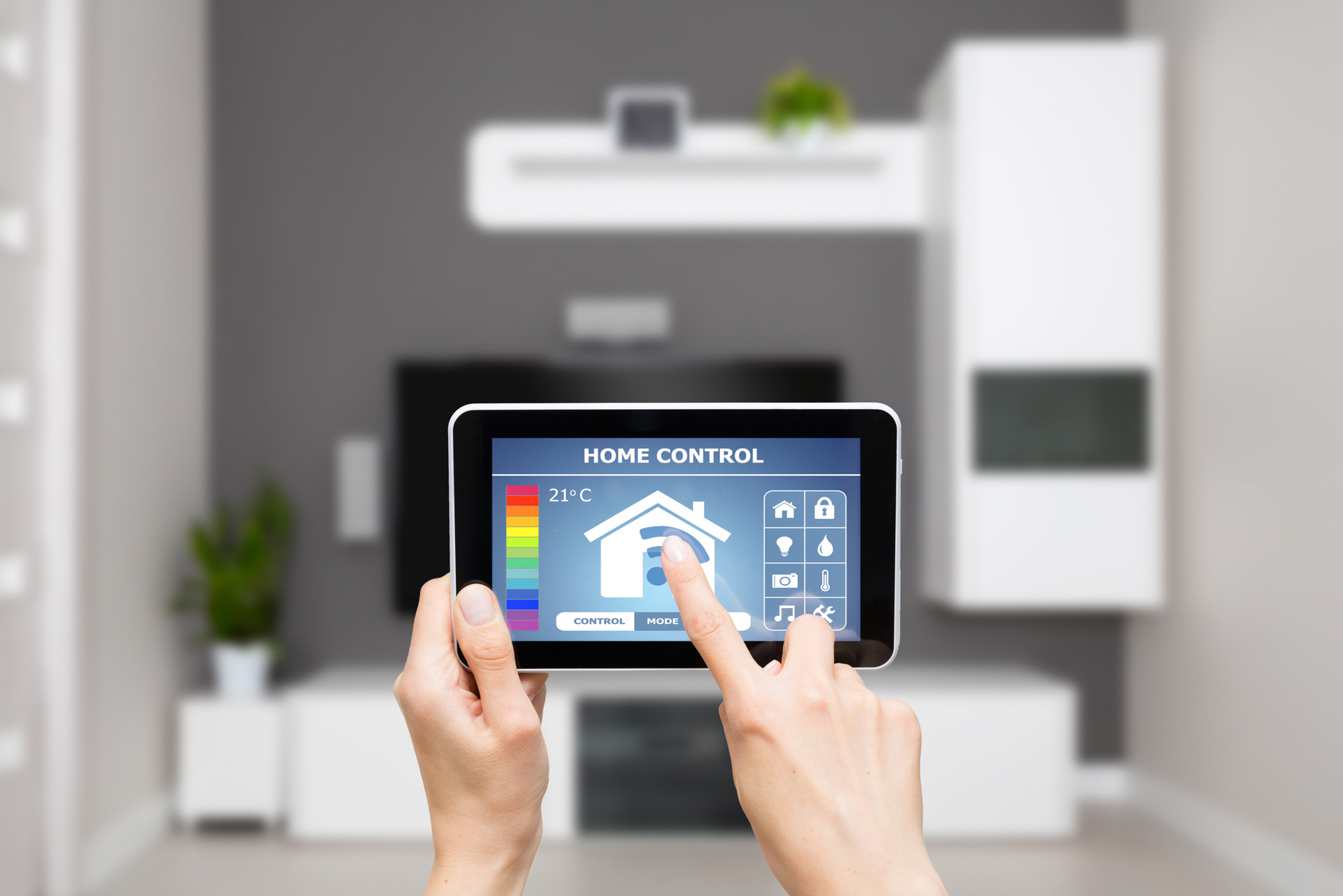
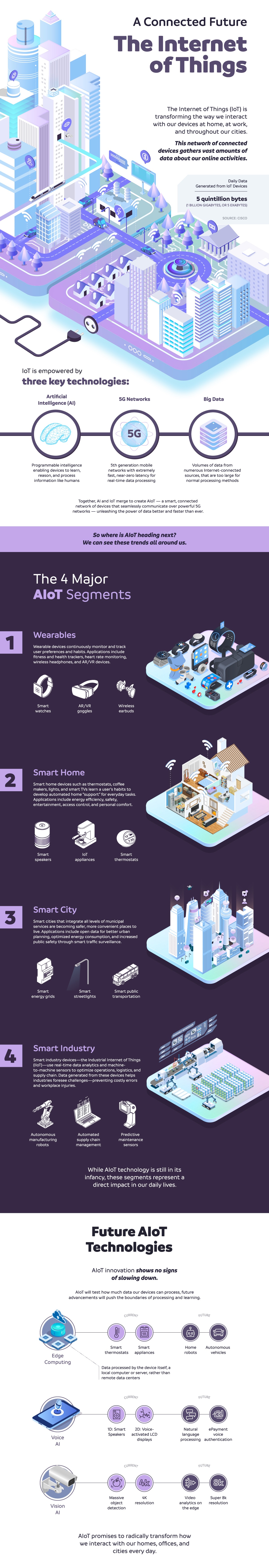
The Internet of Things is defined as inter-networking of physical devices, connected devices, smart devices, and other devices embedded with electronics, software, sensors, actuators, and network connectivity that enable these objects to collect and exchange data.
The IoT allows objects to be sensed or controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, and resulting in improved efficiency, accuracy and economic benefit in addition to reduced human intervention.
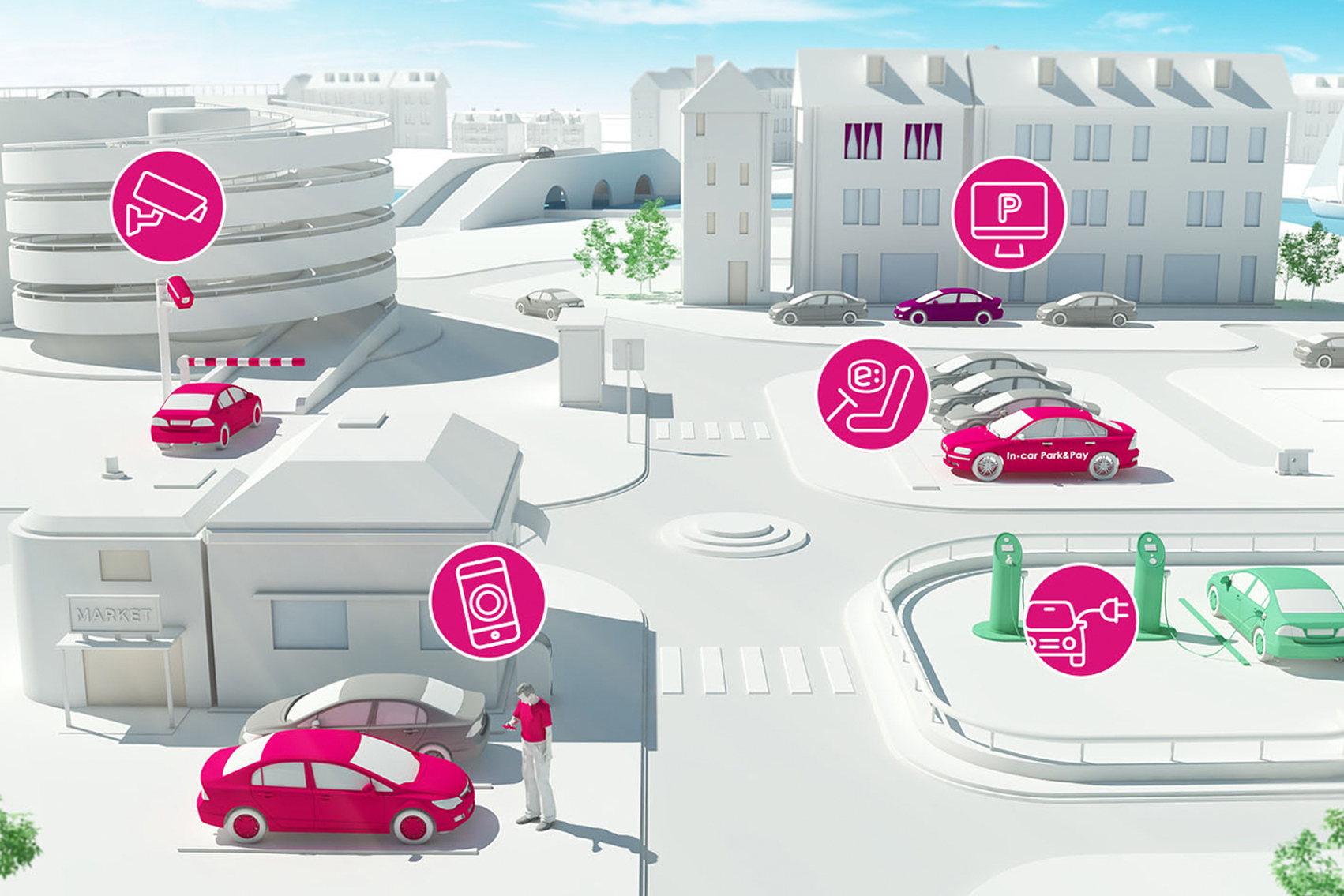
When IoT is augmented with sensors and actuators, the technology becomes an instance of the more general class of cyber-physical systems, which also encompasses technologies such as smart grids, smart homes, intelligent transportation and smart cities.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
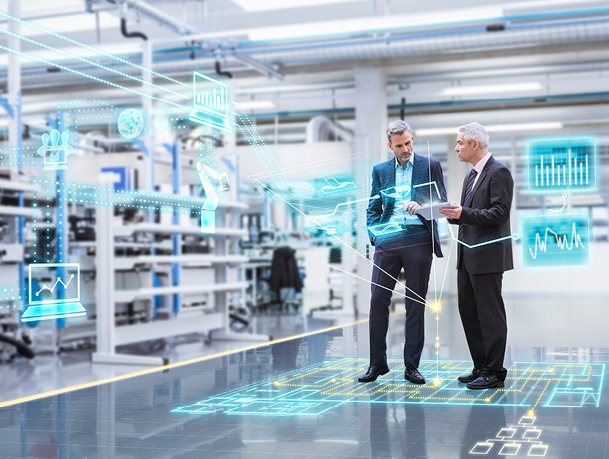

The Industrial IoT (IIoT) adding intelligence to manufacturing equipment, processes, and management. Our smart manufacturing solutions use connected sensors and devices at the network edge to improve machine and human performance in real-time, and pass data to the cloud for deeper analysis and insights. Welcome to Industry 4.0.
Industry 4.0 is a recent technological advances where automation, data exchange, cyber-physical systems, Internet of things, cloud, Big Data and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0 is supposed to be the backbone to integrate physical objects, human actors, intelligent machines, product lines and processes across organizational boundaries a way to make smart industries achieve better manufacturing goals with the use of new technologies and innovations.